Monitoring your blood glucose level is an effective way to manage diabetes as well as gestational diabetes. Here is a guide that will help you understand blood glucose monitoring better.
What is blood glucose level?
It goes by many names including blood sugar level, glycemia, or blood glucose level. Essentially it is the level of glucose (sugar) present in a person’s blood. It is typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl) or millimoles per litre (mmol/l).
Why should you get it checked?
All the nasi lemak (coconut milk rice) and kuih-muih (local desserts and fritters) that we eat are converted to glucose which the body uses to produce energy. Insulin, a hormone produced by our pancreas then ensures the glucose enters our body’s cells. Dysfunctional or absence of insulin can lead to dangerous conditions called hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia also known as diabetes mellitus. Therefore, monitoring the levels of glucose is absolutely vital.
How to test your blood glucose level?
Finger pricking test:

Start by pricking your finger using a small needle called a lancet. Put a drop of blood on a test strip and place the test strip into a blood glucose meter. Your current blood sugar level should be revealed in less than 15 seconds. This test can be done at home or with the assistance of medical professionals. Remember to fast for 8 to 12 hours before testing for accurate results.
Random blood sugar test:

For this test, your blood sample can be taken at any random time with no fasting needed.
Fasting glucose test:
Your blood sample will be drawn by doctors after 8 hours of fasting usually in the morning before breakfast.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT):
This test requires you to fast for 8 hours before you blood sample is sent for testing. After that, you will be given a sugary drink followed by more blood samples taken over the next two to three hours.
Urine glucose test:
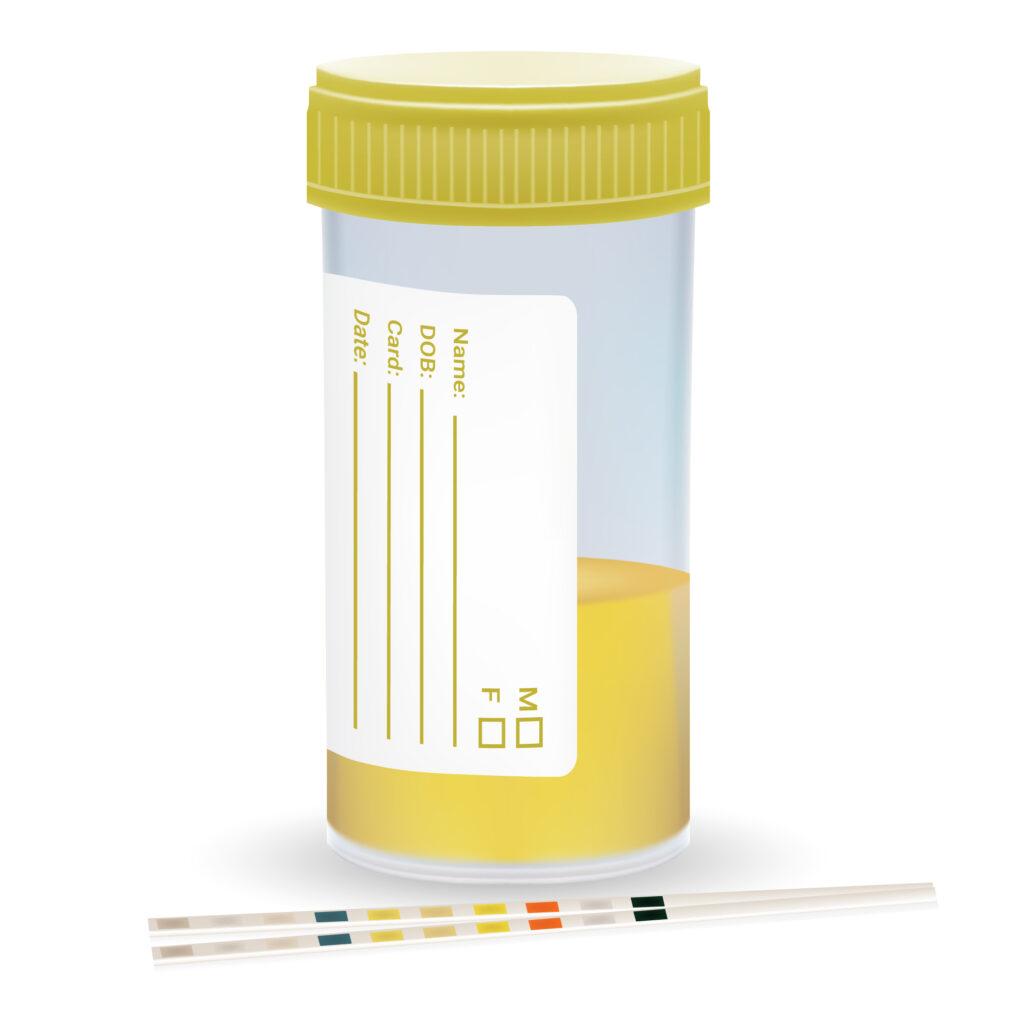
A common symptom of diabetes is glycosuria which is the presence of glucose in the urine. If you are diabetic, all you need to do is read the test strip once it changes colour after reacting with glucose in the urine. You can perform this at home too.
HbA1c test:

Haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) or A1c test measures the amount of blood sugar attached to your haemoglobin over the last three months. This method is used to diagnose diabetes, and help monitor if you’re at risk of developing diabetes. You can get this done every three to six months with your doctor.
Flash glucose monitors and Continuous glucose monitors (CGM):
A CGM connects to your mobile via Bluetooth to show your latest sugar levels while a flash glucose monitor requires you to wave (scan) your device over your sensor to get your blood sugar readings. This real-time technology allows you and your healthcare team to monitor and alter your treatment.
How to test your blood glucose level?
NORMAL
Fasting (before food):
4.0 – 6.0 mmol/l
Random:
4.4 – 8.0 mmol/l
ABNORMAL
Hyperglycemia:
11.1 mmol/l
Hypoglycemia:
<2.8 mmol/l
Sources: WebMD, Mayo Clinic, NHS, Diabetes UK, MEDS, DoctorOnCall, MyHealth











